Why do some international conflicts last for decades while others get resolved quickly? The answer often lies in how nations approach negotiation.
When countries face disputes over borders, trade, or political differences, military force isn’t the only option. Smart diplomacy through negotiation can prevent wars and save millions of lives.
In this blog, I’ll show you how negotiation works in international conflicts.
You’ll learn the key principles that make diplomatic talks successful and see real strategies that help nations find peace instead of fighting.
Why Negotiation Matters in International Conflicts?
Negotiation serves as the first line of defense against war. When nations choose to talk instead of fight, they protect their people and economies from destruction.
History shows us that negotiated solutions last longer than forced ones. The Camp David Accords between Egypt and Israel, signed in 1978, established a peace that remains in effect today.
This happened because both sides agreed to the terms willingly.
Benefits of negotiation over warfare:
- Saves human lives and prevents refugee crises
- Protects economic resources and trade relationships
- Builds trust between nations for future cooperation
- Creates legally binding agreements that both sides respect
- Allows face-saving solutions for all parties involved
Countries that negotiate well also strengthen their international reputation. Other nations see them as reasonable partners for future deals.
Key Principles of Diplomatic Negotiation
Successful international negotiation follows specific principles that help countries reach agreements. These principles guide diplomats through complex talks.
Core negotiation principles:
- Mutual respect – Both sides treat each other as equals
- Transparency – Open sharing of concerns and goals
- Flexibility – Willingness to adjust positions when needed
- Patience – Understanding that complex issues take time
- Good faith – Honest commitment to finding solutions
- Confidentiality – Keeping sensitive discussions private
- Cultural awareness – Respecting different traditions and values
These principles are effective because they create an environment where both parties feel heard. When countries follow these rules, they establish trust that enables agreements to be possible.
Steps in Negotiating Treaties or Agreements
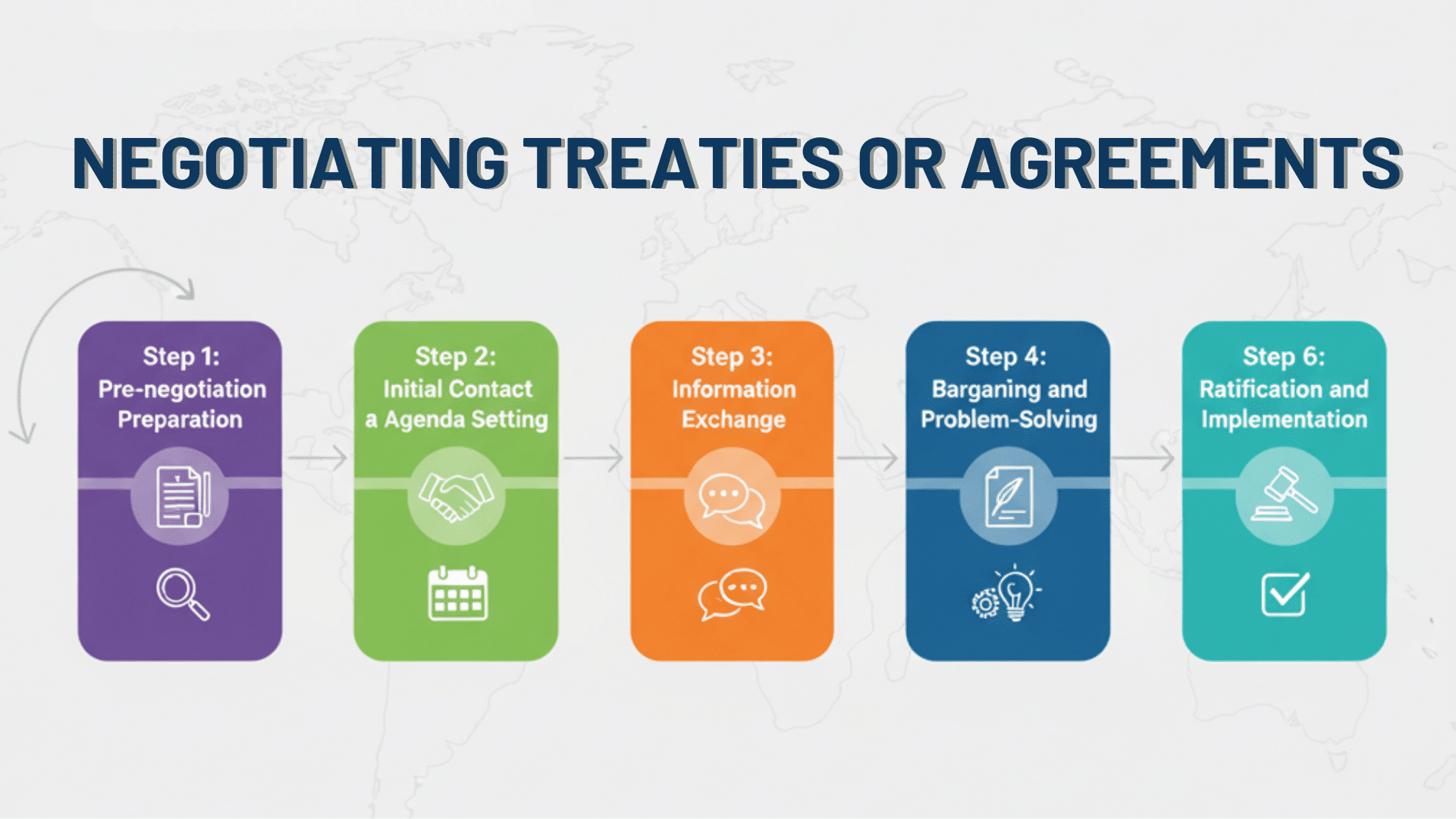
International negotiations follow a structured process that facilitates countries’ transition from conflict to cooperation. Here’s how diplomatic teams typically work:
Step 1: Pre-negotiation preparation: Countries research each other’s positions and set clear goals before talks begin. They also build support from their own governments and citizens to ensure any agreement will be accepted.
Step 2: Initial Contact and Agenda Setting: Diplomatic teams establish secure communication channels and agree on meeting locations. They decide which specific issues will be discussed and create a timeline for the talks.
Step 3: Information exchange: Both sides share relevant facts and data about the dispute openly. This helps each country understand the other’s concerns and find areas where their interests overlap.
Step 4: Bargaining and problem-solving: Negotiators propose solutions that benefit both countries and make trade-offs between different issues. They test new ideas through informal discussions before making formal offers.
Step 5: Agreement drafting: Legal teams write formal treaty language that both sides can accept. The document includes enforcement mechanisms, timelines, and plans for future reviews or adjustments.
Step 6: Ratification and implementation: Each country gets approval from their parliament or congress to make the agreement official. They create monitoring systems and maintain regular communication to prevent future problems.
Strategies for Resolving Border Disputes Through Negotiation
Border conflicts between nations require special negotiation approaches. These disputes often involve territory, resources, and national identity.
1. Land-Based Border Solutions

Territorial swaps allow countries to trade land of equal value. India and Bangladesh successfully used this method in 2015 to resolve a 68-year border dispute.
Joint administration lets both countries manage disputed areas together. This works well for resource-rich regions where both sides have legitimate claims.
Compensation packages provide economic benefits instead of territory. One country might pay the other for development projects or trade advantages.
2. Maritime Boundary Negotiations

The median line principle divides ocean areas equally between countries with opposite coasts. This method works when the distance between the shores is clear.
Economic zone sharing allows both countries to fish or extract resources from disputed waters. They split the benefits without changing legal boundaries.
International arbitration brings in neutral experts to decide boundary lines. The Permanent Court of Arbitration helps many countries resolve maritime disputes.
3. Resource-Sharing Agreements

Water rights treaties help countries share rivers and lakes that cross borders. The Indus Waters Treaty between India and Pakistan has worked since 1960.
Mining concessions let both countries benefit from mineral resources in border areas. Joint ventures can be more profitable than fighting over territory.
Negotiation vs Mediation in Diplomacy
Understanding the distinction between negotiation and mediation enables countries to select the most suitable approach for their disputes.
| Aspect | Negotiation | Mediation |
|---|---|---|
| Participants | Only the conflicting countries | Third party helps facilitate |
| Control | Countries control the process | Mediator guides discussions |
| Timeline | It can take months or years | Usually faster resolution |
| Costs | Lower – just diplomatic teams | Higher – need neutral mediators |
| Privacy | Complete confidentiality possible | May involve public pressure |
| Binding power | Agreements are legally binding | Depends on which countries accept |
| Success rate | 60-70% for willing parties | 80-85% with skilled mediators |
When to use negotiation:
Direct negotiation is most effective when both parties genuinely desire to resolve their differences through open and honest dialogue.
This approach is most effective for straightforward disputes between nations that already maintain good diplomatic relationships and have sufficient time to work through the issues carefully.
When to use mediation:
Mediation becomes necessary when previous direct talks have collapsed or when emotions between countries run too high for productive dialogue.
It’s also the preferred method for complex disputes involving multiple nations or when the resolution needs public legitimacy through neutral oversight.
Lessons from Failed Negotiations
Learning from unsuccessful diplomatic efforts helps countries avoid similar mistakes in future conflicts.
| Case Study | Time Period | Reason for Failure | Key Lesson |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camp David II | 2000 | Both sides had unrealistic expectations and didn’t build trust before tackling hard issues | Start with easier problems to build momentum before addressing core disputes |
| North Korea Nuclear Talks | 1990s-2000s | North Korea made promises it couldn’t keep, causing other countries to lose trust | Agreements need verification systems to ensure both sides follow through |
| Brexit Negotiations | 2016-2020 | UK government changed positions multiple times due to internal political conflicts | Countries need stable internal support before entering international negotiations |
Common reasons negotiations fail:
- Unrealistic demands from one or both sides
- Lack of trust between negotiating teams
- External pressure from media or public opinion
- Changes in government during talks
- Hidden agendas not shared with the other side
- Cultural misunderstandings and communication problems
The Bottom Line
Negotiation plays a vital role in resolving conflicts between nations and maintaining global peace. Countries that choose dialogue over confrontation build stronger relationships and create lasting solutions.
Successful negotiations require preparation, patience, and mutual respect.
When nations follow proven principles and learn from past experiences, they can resolve even the most complex disputes peacefully. History shows that discussing problems works better than arguing over them.
Diplomatic skills are more important than ever in today’s interconnected world. Small disagreements can quickly escalate into major problems without effective negotiation.
What examples of successful international negotiations inspire you most? Share your thoughts below.