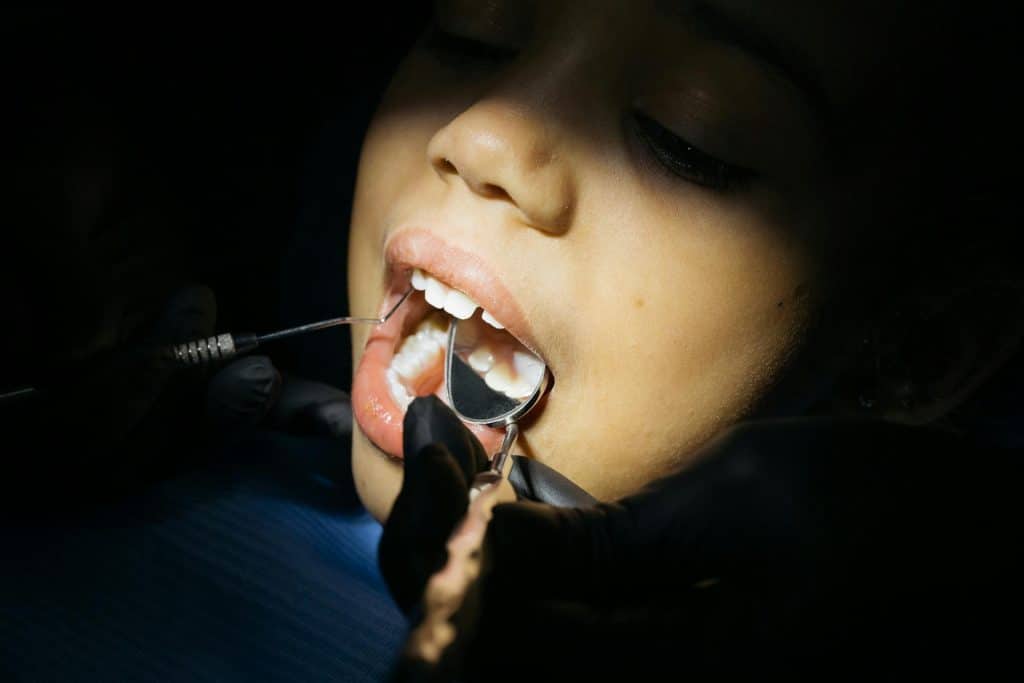
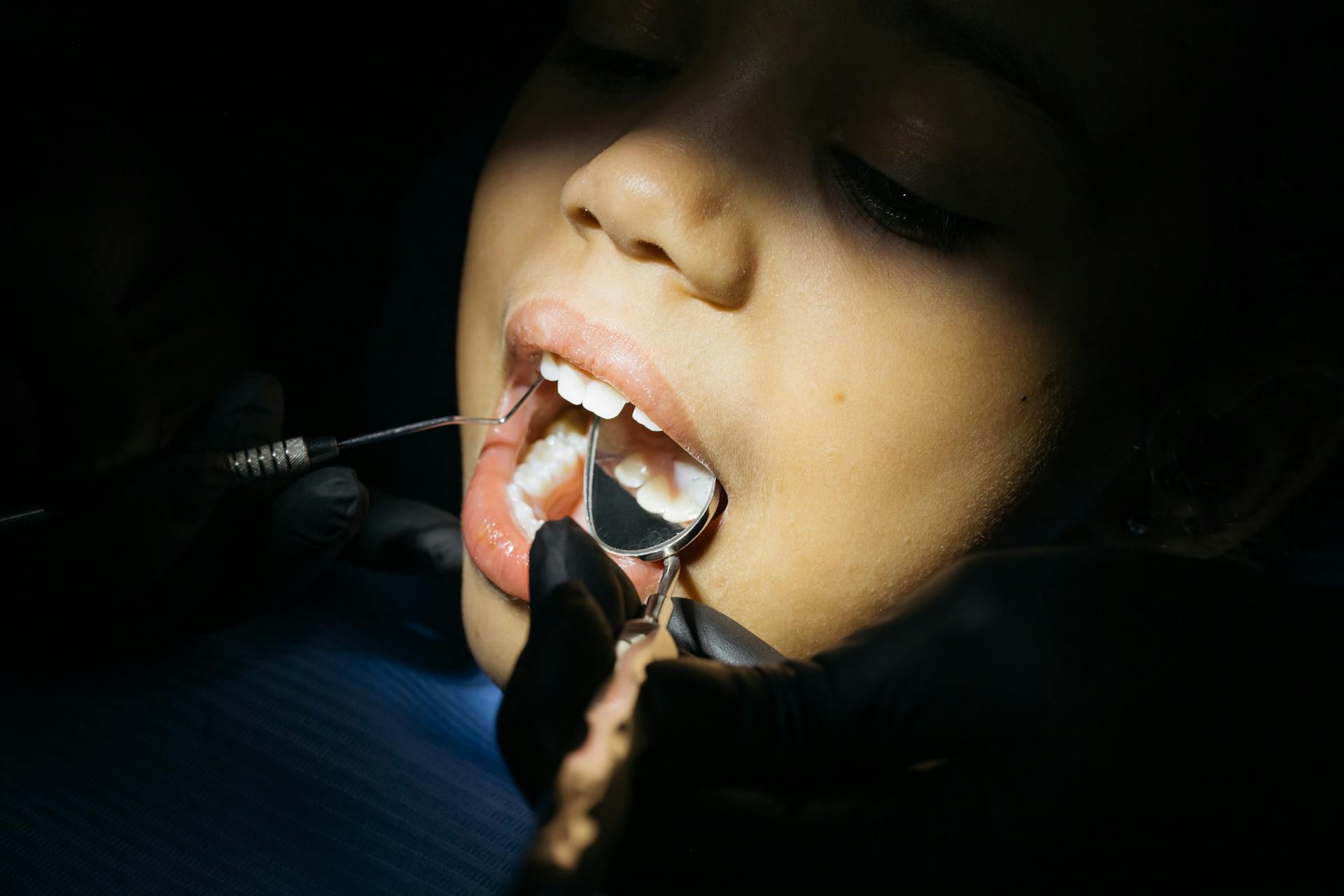
Gum problems often start subtly. A little bleeding while brushing or slight gum tenderness may not seem alarming at first. Yet these early signs frequently signal the beginning of gum disease, a condition that affects a large portion of adults and teens alike. Without timely care, gum disease can progress silently and lead to tooth loss, chronic infection, and broader health concerns.
Understanding gum disease treatment options empowers patients to act early and choose the right level of care. In Singapore, dentists increasingly emphasize prevention and early intervention, helping patients manage gum disease before it becomes complex or costly. This guide explains how dentists approach gum disease treatment, what options truly work, and when professional care becomes essential.
What Causes Gum Disease in the First Place?
Gum disease develops when bacteria in dental plaque build up along and below the gum line. If plaque is not removed effectively, it hardens into tartar, triggering inflammation and infection.
Several factors increase the risk of gum disease:
- Inconsistent oral hygiene routines
- Smoking or vaping habits
- Medical conditions such as diabetes or hormonal changes
While genetics can play a role, daily habits and professional dental care largely determine whether gum disease progresses or remains under control.
Stages of Gum Disease and Why Early Treatment Matters
Dentists classify gum disease into stages based on severity. Each stage requires a different treatment approach.
Gingivitis: The Early and Reversible Stage
Gingivitis causes redness, swelling, and bleeding gums. At this stage, no permanent damage has occurred. Professional cleaning combined with improved home care often reverses the condition completely.
Early gum disease treatment focuses on eliminating plaque and reducing inflammation. Patients who act quickly avoid long-term complications.
Periodontitis: Advanced Gum Disease
When gingivitis goes untreated, it can progress into periodontitis. Infection spreads deeper, damaging bone and connective tissue. Gums may recede, and teeth can become loose.
At this stage, gum disease treatment becomes more involved and requires ongoing professional care to prevent further damage.
Common Warning Signs You Should Not Ignore
Many patients underestimate gum disease because it often develops without pain. Dentists encourage patients to watch for subtle but persistent changes.
Signs that indicate the need for gum disease treatment include:
- Bleeding during brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath or a bad taste
- Gums pulling away from teeth
Seeking care when these signs appear allows dentists to intervene before irreversible damage occurs.
Professional Gum Disease Treatment Options Explained
Routine Dental Cleaning and Scaling
For mild gum disease, professional cleaning remains the first line of treatment. Dentists remove plaque and tartar from above and just below the gum line, allowing gums to heal naturally.
Regular scaling appointments also help prevent recurrence when combined with proper home care.
Scaling and Root Planing for Moderate Disease
When bacteria settle deeper beneath the gums, dentists recommend scaling and root planing. This deep-cleaning procedure removes hardened deposits from root surfaces and smooths them to discourage bacterial regrowth.
Scaling and root planing often resolve moderate gum disease without surgery and remain a cornerstone of effective gum disease treatment.
Advanced Treatment Options for Severe Gum Problems
Periodontal Maintenance Therapy
For patients with recurring or advanced gum disease, dentists create structured maintenance plans. These involve more frequent cleanings, monitoring gum pocket depth, and adjusting treatment as needed.
This long-term approach helps stabilize gum health and slows disease progression.
Surgical Gum Disease Treatment
When non-surgical methods no longer control infection, surgical treatment may become necessary. Procedures aim to reduce deep pockets, regenerate bone, or reshape gum tissue for easier cleaning.
Dentists only recommend surgery when clinically necessary, and modern techniques focus on precision and patient comfort.
The Role of Home Care in Supporting Treatment
Professional treatment alone cannot control gum disease. Daily habits play a decisive role in long-term success.
Effective home care supports gum disease treatment by:
- Removing plaque daily before it hardens
- Reducing inflammation between dental visits
- Preventing bacteria from recolonizing gum pockets
Dentists often provide personalized oral hygiene guidance to ensure patients maintain results at home.
When to See a Dentist for Gum Disease Treatment
Patients should not wait for pain before seeking help. Gum disease often advances silently until significant damage occurs.
Seeing a dentist promptly is essential if bleeding persists, gums recede, or teeth feel unstable. Regular dental check-ups in Singapore allow early detection and simpler treatment options.
Gum Disease Treatment in Singapore: What Patients Can Expect
Singapore’s dental clinics operate under strict professional standards set by the Ministry of Health. Dentists rely on evidence-based protocols and modern diagnostic tools to assess gum health accurately.
Urban lifestyles, stress, and dietary habits contribute to gum disease locally, making preventive care especially important. Many clinics integrate periodontal screening into routine dental visits, helping patients address gum issues early.
Long-Term Benefits of Timely Gum Disease Treatment
Treating gum disease early protects both oral and overall health. Healthy gums support strong teeth, improve comfort, and reduce the risk of future dental procedures.
Effective gum disease treatment also supports:
- Better chewing and speech function
- Improved confidence and oral comfort
- Lower long-term dental costs
Patients who commit to ongoing care experience more stable and predictable outcomes.
Key Insights on Managing Gum Disease Successfully
Gum disease treatment works best when patients combine professional care with consistent home habits. Not every treatment suits every case, which makes personalized dental assessment essential.
Dental providers that emphasize prevention, education, and ethical care—such as those associated with trusted groups like Nuffield Dental, reflect a modern approach focused on preserving gum health rather than managing advanced disease.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can gum disease treatment completely cure the condition?
Early-stage gum disease can be reversed, while advanced cases can be managed and stabilized with ongoing care.
2. How painful is gum disease treatment?
Most treatments involve minimal discomfort, and dentists use modern techniques to keep patients comfortable.
3. How long does gum disease treatment take?
Treatment length depends on severity, ranging from a few weeks for mild cases to ongoing maintenance for advanced disease.
4. Can gum disease return after treatment?
Yes, without proper oral hygiene and regular dental visits, gum disease can recur.
5. How often should I visit a dentist if I have gum disease?
Patients with gum disease may need more frequent visits, often every three to four months, based on their condition.