Have you ever wondered how wars are being fought beyond physical battlefields? Today’s conflicts happen through computer screens and internet connections.
Nations attack each other using code instead of bombs.
Cyber warfare has become one of the most serious threats facing our world. Countries spend billions defending their digital borders.
Major attacks can shut down power grids, steal state secrets, or disrupt elections.
In this blog, I’ll explain what cyber warfare is and why it matters. You’ll learn about real-world attacks, understand how these digital weapons work, and see how nations counter them.
By the end, you’ll have a clear view of this invisible war happening around us.
What Is Cyber Warfare?
Cyber warfare is the use of digital attacks by one nation against another nation’s computer systems. The main goal is to damage, disrupt, or gain access to enemy networks and data.
Unlike traditional warfare with soldiers and weapons, cyber warfare uses:
- Malicious software to break into systems
- Hackers trained by governments
- Computer code as the main weapon
- Internet connections as the battlefield
Differences of Cyber Warfare from Traditional War

The contrast between old-style fighting and cyber warfare is evident when they are compared side by side.
| Traditional Warfare | Cyber Warfare |
|---|---|
| Physical weapons | Digital weapons |
| Visible damage | Hidden attacks |
| Clear battlefields | Invisible networks |
| Soldiers in uniform | Anonymous hackers |
The main goals of cyber warfare include:
- Espionage: Stealing government secrets and military plans
- Disruption: Shutting down critical services like power or water
- Sabotage: Destroying important computer systems
- Information warfare: Spreading false news to confuse people
Examples of Cyber Warfare in Action
Real cyber attacks have changed how nations think about security. Here are some major cases that shook the world:
| Attack Name | What Happened |
|---|---|
| Stuxnet (2010) |
|
| SolarWinds Hack (2020) |
|
| NotPetya Attack (2017) |
|
| Election Interference (2016-Present) |
|
How Cyber Warfare Works?
Cyber warfare utilizes computer networks as a means of attack against enemy nations.
Unlike traditional wars with bombs and guns, these digital battles happen through internet connections. Attackers break into important systems to steal secrets, cause damage, or disrupt daily life.
The process typically involves three steps: hackers first identify weak points in target systems, then exploit these vulnerabilities using various attack methods, and finally achieve their objectives, such as stealing data or disrupting services.
Various Cyber Attack Methods
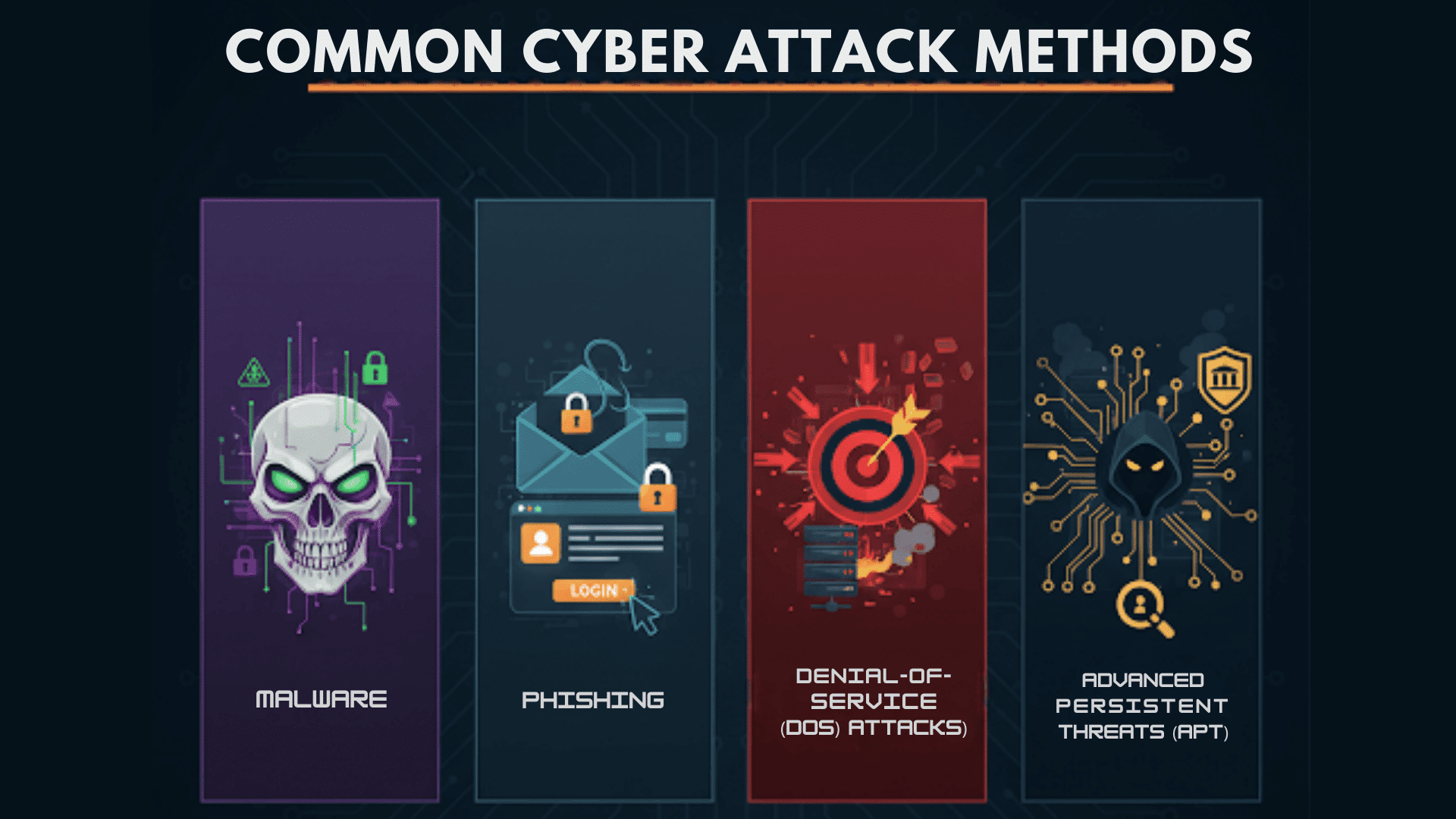
Various cyber attack methods include:
- Malware: Harmful software that damages systems or steals data. This includes viruses, ransomware that locks files for payment, and spyware that secretly collects information.
- Phishing: Fake emails and websites that trick people into sharing passwords or personal details. These messages often install malware when clicked.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Flooding websites with fake traffic to shut them down. This makes services unavailable and often distracts from other attacks.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APT): Long-term hidden attacks that slowly explore networks for valuable data. Government agencies often sponsor these sophisticated operations.
Primary Targets of The Cyber Attackers
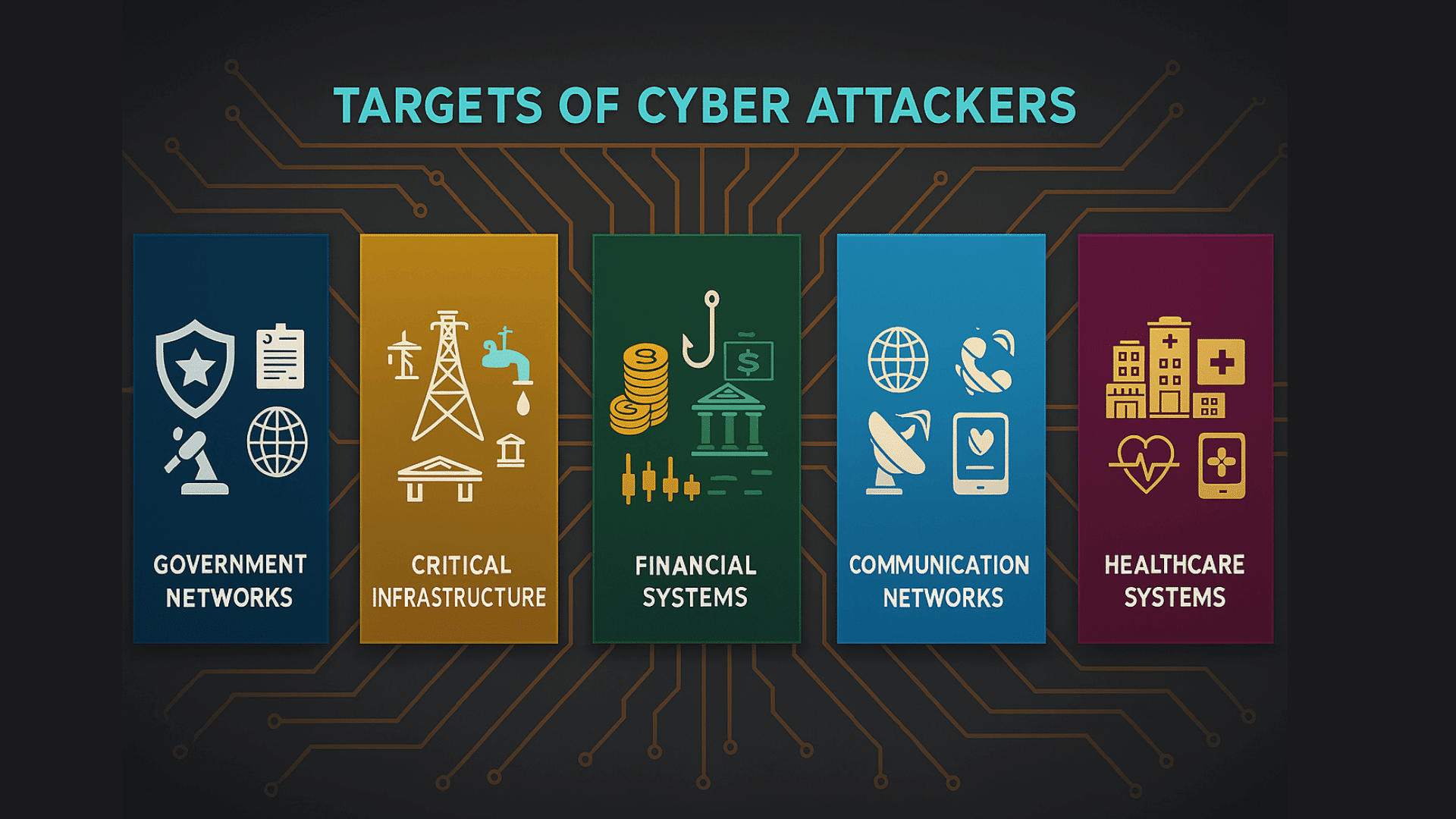
Cyber warfare typically focuses on these critical areas:
- Government networks: Military secrets, diplomatic communications
- Critical infrastructure: Power grids, water systems, transportation
- Financial systems: Banks, stock markets, payment processors
- Communication networks: Internet providers, phone systems
- Healthcare systems: Hospitals, medical records, emergency services
How Countries Fight Back Against Cyber Attacks?
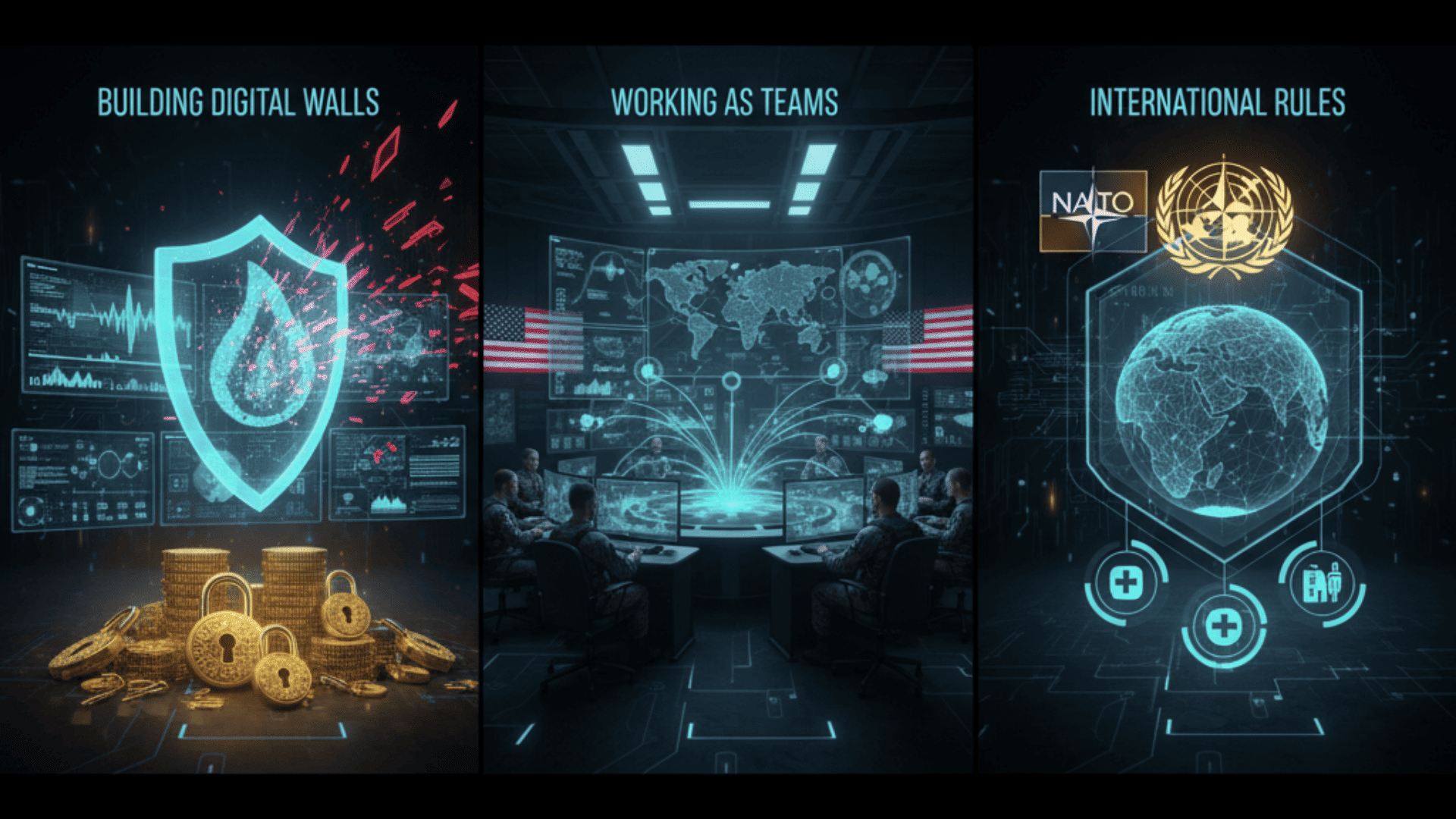
Nations employ three primary approaches to protect themselves from cyber warfare: building robust digital defenses, collaborating as teams, and establishing international regulations.
1. Building Digital Walls
Countries install firewalls that block dangerous internet traffic before it reaches important systems. AI detection systems watch networks 24/7, spotting unusual behavior.
Encryption scrambles sensitive information like a secret code. Even if hackers steal files, they cannot access the data without the correct key.
2. Working as Teams
Major nations have established cyber command centers, which are military units focused on digital threats. The U.S. Cyber Command and Britain’s cyber center coordinate defenses.
Countries share information about new threats they discover. When one nation identifies dangerous hackers, it warns others to strengthen their defenses.
3. International Rules
NATO members assist one another during major cyberattacks, treating digital assaults as they would physical attacks on their territory. This creates collective defense against threats.
The United Nations creates global rules about cyber warfare. They decide what counts as an attack and which targets remain off-limits, such as hospitals.
The Future of Cyber Conflict
Cyber warfare is constantly evolving as technology advances. Artificial Intelligence makes attacks smarter but also helps defenders spot threats faster.
Quantum Computing will render current security methods obsolete, giving an advantage to countries that develop it first.
More connected devices, like smart homes and cloud services, create new targets. When attacked, millions of people can be affected at once.
Staying protected requires:
- Strong passwords and updated software for individuals
- Employee training and response plans for organizations
- Constant adaptation to new threats
Conclusion
Cyber warfare has changed the way nations conduct conflicts. Unlike traditional wars, these digital battles affect everyone online.
Attacks like Stuxnet and SolarWinds demonstrate how malicious code can compromise real-world infrastructure and steal sensitive information.
Understanding cyber warfare helps us see why this invisible war matters. Nations keep building better defenses through AI systems and international cooperation.
New technologies like quantum computing will make future attacks and defenses even stronger.
As our world becomes increasingly connected, cybersecurity becomes more crucial.
Do you think the next major global conflict will be fought more online than on the ground? The answer might shape how we prepare for future security challenges.