What does it really mean to have rights under the U.S. Constitution? For many people, these protections feel like abstract ideas tucked away in history books.
In reality, they shape your daily life in ways you may not even notice. The freedom to speak openly, the right to a fair trial, or the guarantee of equal treatment under the law all come directly from this living document.
These rights define what it means to be free in the United States of America.
In this blog, I’ll show you how constitutional protections work, why they matter, and how they continue to safeguard your everyday freedoms.
What Are Constitutional Rights?
Your Rights Under the U.S. Constitution are promises the government makes to you. These rights come from the Bill of Rights and other amendments.
Understanding Your Rights Under the U.S. Constitution helps you recognize when these protections apply in your daily life.
The Constitution works like a contract between you and your government. The government gets the power to run the country. In return, it must protect your basic rights.
Key facts about constitutional rights:
- They apply to all citizens and many non-citizens
- State and local governments must follow them too
- Courts protect these rights when they’re violated
- Some rights have limits during emergencies
Constitutional rights fall into two main groups:
- Civil Liberties : These are freedoms that protect you from government interference, like speaking your mind, practicing your religion, and being safe from unreasonable searches in your home.
- Civil Rights: These ensure the government treats all people fairly and equally, providing due process in legal matters and protecting you from discrimination based on race, gender, or other characteristics.
These rights come from the Bill of Rights and other amendments. The Bill of Rights includes the first ten amendments to the Constitution. These were added in 1791 to protect individual freedoms.
The First Amendment: Your Core Freedoms
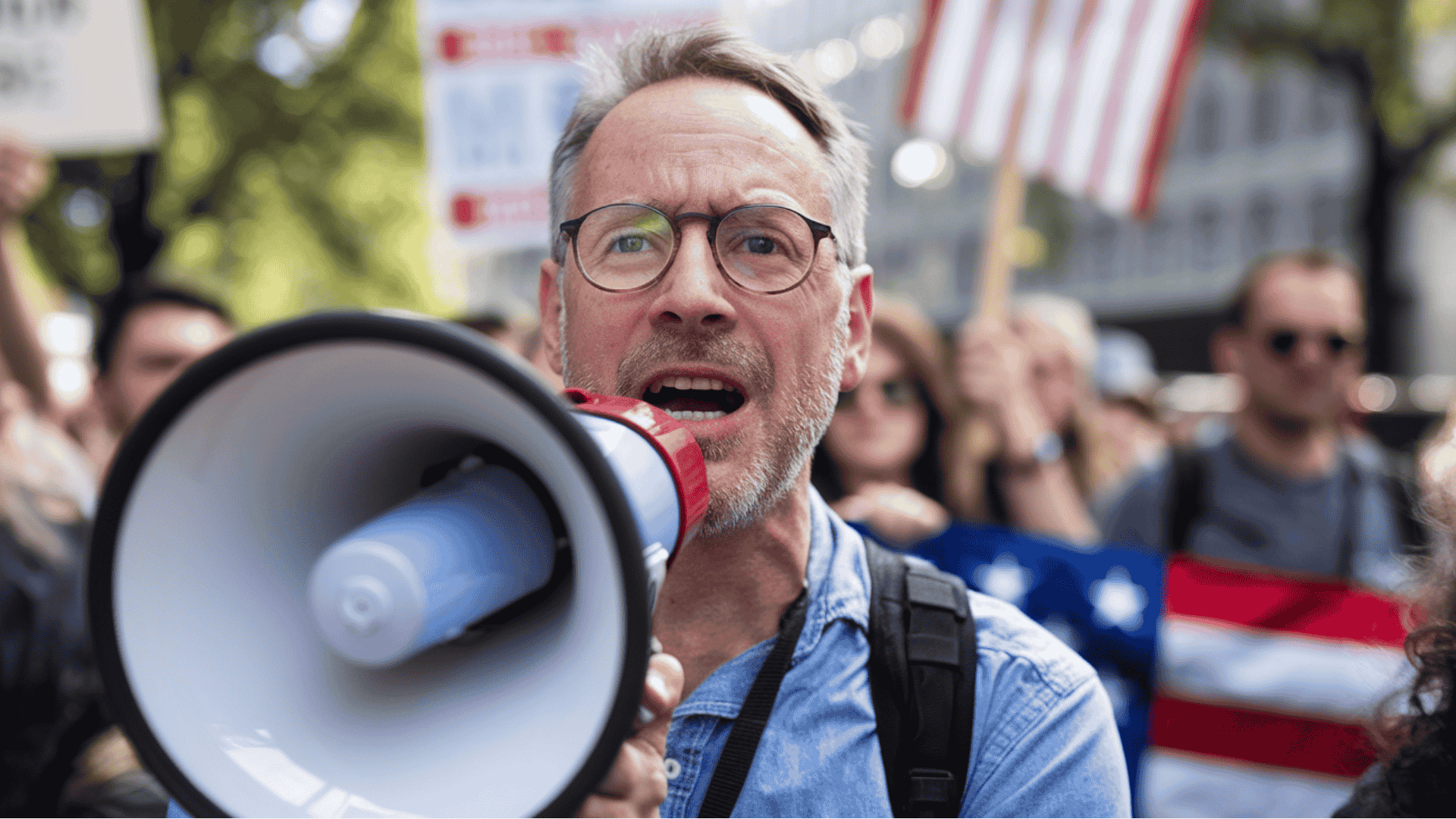

Rights under the First Amendment protect your most basic freedoms. This single amendment addresses five key areas that significantly impact your daily life.
1. Freedom of Speech
You can express your opinions through verbal speech, written words, symbolic actions such as clothing choices, and political criticism without facing government punishment.
However, threats of violence, false statements that harm reputations, speech creating immediate danger, and obscenity in certain public spaces are not protected.
2. Freedom of Religion
You can worship how you choose, follow your beliefs, refuse other religions, and change your faith anytime without government interference. The government cannot establish an official religion or stop you from practicing your faith freely.
3. Freedom of the Press
News organizations can report on government actions, conduct investigations, publish opinions, and operate online without fear of government retaliation. The independent press keeps the government accountable and informs citizens about important issues.
4. Freedom of Assembly
You can join protests, political rallies, religious services, and social organizations as long as they remain peaceful. The government cannot stop you from meeting with others who share your views or interests.
5. Freedom to Petition
You can write to elected officials, sign petitions, attend town halls, and file lawsuits to address government problems. This right ensures citizens can demand action when the government fails to serve their needs.
These First Amendment rights work together to maintain a strong democracy. They let you participate in government and hold leaders accountable.
Due Process and Equal Protection: Your Legal Safety
What is due process? It’s your right to fair treatment in the legal system. Equal protection means the government must treat everyone fairly under the law. Together, they form a safety net that shields your freedoms every day. There are two key forms of due process:
-
Procedural – Fair treatment in legal proceedings. You have the right to know charges, defend yourself, and get a fair hearing with legal representation.
-
Substantive – Limits on what government can do. You’re protected from unfair laws, invasion of privacy, and unjust restrictions on property or personal choices.
Equal Protection Rights Explained
The government cannot treat people differently based on certain characteristics. The same laws must apply to everyone, whether rich or poor, ensuring equal treatment in the eyes of the law.
It also means that discrimination based on race, gender, or religion cannot determine the rights you are entitled to.
Equal protection guarantees fair access to public services, such as schools and government programs, and secures the right of all eligible citizens to participate in elections.
When Due Process Matters Most
Due process becomes especially important when you face legal trouble. In criminal cases, it guarantees that you are considered innocent until proven guilty. In civil lawsuits, it ensures both sides are treated equally in court.
During government hearings, it gives you the chance to present your side of the story, and through the appeals process, it allows you to challenge decisions that seem unfair.
Due process and equal protection work as your safety net. They ensure the system treats you fairly, regardless of your background or circumstances.
Your Rights in Action

Your Rights Under the U.S. Constitution only matter if you can use them in real life. Here are some everyday situations where constitutional protections apply.
Rights of Protestors Explained
You have the right to protest peacefully in public spaces. Marching, speaking out, and gathering are protected, but violence, trespassing, or blocking traffic are not. Stay peaceful, and the law stays on your side.
Your Right to Legal Counsel
If you are arrested or charged, you have the right to a lawyer. If you can’t afford one, the court must provide it in serious cases. Ask clearly for an attorney and stop talking until they arrive.
Rights of Search and Seizure
Police usually need a warrant or probable cause to search you or your home. They can act without one only in limited situations, like emergencies or when you give permission.
If you’re searched unfairly, don’t resist, just state that you do not consent and contact a lawyer.
Airport Security and Your Rights
At airports, TSA officers have broader powers. They can screen bags, use scanners, and confiscate items. You may request a private screening or ask for a supervisor if needed, but travel is treated as a privilege, so protections are more limited.
Knowing how your rights work in daily life helps you stay protected when challenges arise. The more you understand them, the more confident you’ll be in standing up for yourself.
When to Act: Challenging Rights Violations
Sometimes you must take action to protect Your Rights Under the U.S. Constitution. Knowing when and how to act can make the difference between losing your rights and keeping them safe.
| Situation | Warning Signs | What to Do | Who Can Help |
|---|---|---|---|
| Police encounters | Illegal searches, no explanation for the stop, denial of a lawyer, and excessive force | Stay calm, assert your rights, document details, and contact a lawyer | Criminal defense lawyers, ACLU |
| Work or school | Punishment for political views, religious bias, unfair treatment, and restrictions on speech | Record incidents, file complaints, seek legal advice | Employment lawyers, Legal Aid, and civil rights groups |
| Government interactions | Denied services, unequal treatment, lack of due process, blocked access to meetings | Keep records, report violations, and challenge decisions through proper channels | Civil rights attorneys, public interest lawyers |
| Next steps | After any violation | File formal complaints, consult organizations, and use free legal resources | ACLU, Legal Aid Society, state bar, law clinics |
Remember: Your constitutional rights only work if you’re willing to defend them. Taking action when they’re violated protects not just you, but future generations of Americans.
Conclusion
Knowing Your Rights Under the U.S. Constitution empowers you to live freely and defend democracy. They are living protections that influence your choices and freedoms every single day.
The First Amendment gives you the power to speak your mind, practice your faith, and gather with others. Due process and equal protection ensure that justice is fair and equal, no matter who you are.
These safeguards shape how laws are applied, how courts decide cases, and how citizens live freely. But rights only remain strong when they are understood and defended.
What constitutional right do you think affects your daily life the most? Have you ever encountered a situation where you weren’t sure if your rights were being respected?
Understanding these moments helps us all become better-informed citizens and protectors of freedom.