Can art concerts and student exchanges really change international politics?
While traditional diplomacy focuses on formal treaties and trade agreements, cultural diplomacy leverages the power of shared human experiences to foster connections between nations.
From China’s Confucius Institutes to the United States’ Fulbright programs, countries worldwide are utilizing culture as a diplomatic tool. This soft power approach creates connections that go beyond government meetings.
In this blog, I’ll demonstrate how cultural diplomacy operates, its significance, and its subtle influence on the relationships between countries worldwide.
What Is Cultural Diplomacy?
Cultural diplomacy is the practice of utilizing the arts, education, language, and cultural exchanges to foster relationships between countries.
Unlike traditional diplomacy, which often takes place in meeting rooms, cultural diplomacy engages with ordinary people through various means, including exhibitions, exchange programs, language teaching, sports events, heritage projects, and cultural exchange.
Think of it as countries introducing themselves to the world through their best cultural offerings.
When people experience another country’s music, food, or traditions, they often develop positive feelings toward that nation.
Why Cultural Diplomacy Matters in Global Relations?
Cultural diplomacy fosters lasting bonds that endure even the most significant political shifts. Here’s why it’s so effective:
- Builds Trust Between People: Personal connections formed through cultural exchange often outlast government tensions. Students who study abroad become informal ambassadors for life.
- Creates Soft Power Influence: Countries gain influence not through force, but through attraction. People naturally gravitate toward cultures they admire and understand.
- Reduces Stereotypes and Prejudices: Direct cultural contact breaks down misconceptions. When people experience authentic culture, media stereotypes lose their power.
- Opens Economic Opportunities: Cultural familiarity leads to business partnerships. Companies prefer working with countries whose citizens they know and trust.
Regional Examples of Cultural Diplomacy in Action
Countries around the world use different cultural strengths and historical connections to build international relationships through various approaches.
1. North America
These examples show how North American countries leverage their multicultural identities and educational excellence:
- United States: Fulbright scholarships send students worldwide
- Canada: Promotes bilingual identity and multiculturalism globally
2. Europe
European nations often use their rich cultural heritage and established institutional networks:
- France: Alliance Française teaches French language and culture in 137 countries
- Germany: Goethe Institut operates cultural centers worldwide
- United Kingdom: British Council promotes the English language and British culture
3. Asia-Pacific
Asian countries increasingly combine traditional culture with modern pop culture exports:
- China: Confucius Institutes teach Chinese language and culture
- Japan: Cool Japan initiative exports anime, manga, and pop culture
- South Korea: Korean Wave (Hallyu) spreads K-pop and Korean dramas globally
4. Middle East & Africa
These regions often draw on historical connections and shared cultural experiences:
- Turkey: Uses historical Ottoman connections for cultural outreach
- Egypt: Promotes Arab culture through film and television
- South Africa: Shares post-apartheid reconciliation experiences
How Countries Use Cultural Diplomacy Strategically
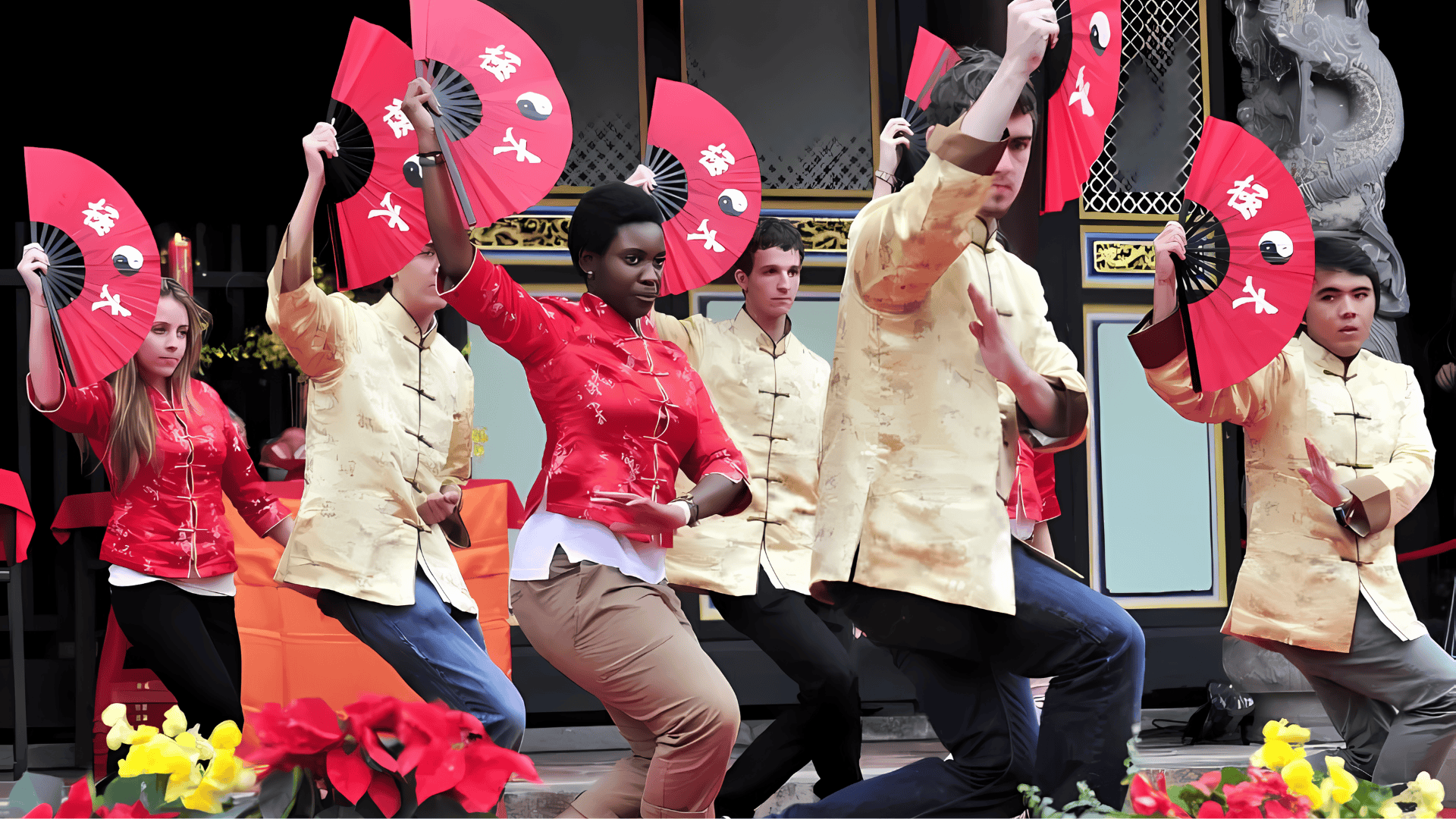

Countries employ cultural diplomacy through several channels:
1. Government Programs
These represent official state-sponsored initiatives that provide direct diplomatic control:
Governments create formal structures to promote their culture worldwide. Cultural attachés at embassies organize events and build partnerships.
Common government approaches include:
- Cultural attachés at embassies
- Official cultural centers abroad
- Sponsored artist residencies
- Heritage site partnerships
These programs give governments direct control over their cultural messaging.
2. Education Programs
These focus on building long-term relationships through knowledge sharing:
Education forms the backbone of long-term cultural influence. Student exchanges create personal connections that last decades.
Popular educational methods include:
- Student exchange programs
- International scholarships
- Foreign language instruction
- Academic partnerships
Universities become cultural ambassadors, sharing knowledge, values and perspectives.
3. Arts and Media
These programs showcase creativity to mass audiences:
Creative industries offer the most visible form of cultural diplomacy. Film festivals showcase national cinema while art exhibitions demonstrate cultural sophistication.
Key strategies include:
- Film festival participation
- International art exhibitions
- Music and dance tours
- Literary translation programs
Entertainment reaches mass audiences in ways government programs cannot.
4. Sports Programs
This approach uses athletic competition to build universal connections:
Sports create connections that cross cultural barriers. Hosting competitions gives countries global visibility.
Main activities include:
- Hosting international competitions
- Athletic exchange programs
- Sports equipment donations
- Training coach exchanges
Sports diplomacy works because athletic achievement transcends politics.
Strategic Benefits Comparison of Cultural Diplomacy Approaches
Different cultural diplomacy approaches offer varying advantages depending on a country’s goals and resources. This comparison enables governments to select the optimal combination of programs tailored to their specific objectives.
| Approach | Time to Impact | Cost | Reach | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Educational Exchange | 5-10 years | High | Limited | Very High |
| Arts Programs | 1-2 years | Medium | Wide | Medium |
| Sports Events | Immediate | High | Very Wide | Low |
| Language Programs | 3-5 years | Medium | Medium | High |
Measuring the Impact of Cultural Diplomacy
Success in cultural diplomacy isn’t always easy to measure, but several indicators help track effectiveness:
- Public Perception Changes:
Regular surveys reveal how foreign publics view different countries. Positive cultural experiences typically improve these ratings over time. - Economic Growth Patterns:
Cultural diplomacy often leads to measurable economic benefits. Tourism increases to culturally active countries, while trade partnerships expand. Foreign direct investment flows increase, and educational service exports rise as countries strengthen their cultural connections. - Media Sentiment Analysis:
Countries with strong cultural programs consistently receive more positive international media attention. News coverage becomes more favorable when nations invest in cultural outreach. - Relationship Durability:
Former exchange participants frequently maintain lifelong connections and become advocates for their host countries. These personal bonds often prove more lasting than formal diplomatic agreements.
Challenges Facing Cultural Diplomacy
Despite its benefits, cultural diplomacy faces several obstacles that can limit its effectiveness.
Knowing these challenges enables countries to design more effective programs and establish realistic expectations for their cultural initiatives.
| Challenge | Key Issue | Main Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Limitations | Programs need long-term funding | Budget cuts damage decades of work |
| Political Interference | Governments use culture for propaganda | Audiences lose trust in programs |
| Cultural Misunderstandings | Poor planning reinforces stereotypes | Creates negative perceptions |
| Competition for Attention | Too many countries are competing globally | Programs get overlooked |
| Measuring ROI | Hard to prove intangible benefits | Officials cut funding support |
Best Practices for Effective Cultural Diplomacy
Successful cultural diplomacy programs share common characteristics:
- Authenticity: Share genuine culture, not manufactured stereotypes
- Reciprocity: Create two-way exchanges rather than one-sided promotion
- Consistency: Maintain programs through political changes
- Local Relevance: Adapt programs to local interests and needs
- Quality Focus: Prioritize excellence over quantity in cultural offerings
The Future of Cultural Diplomacy

Digital technology is transforming the way cultural diplomacy operates. Online cultural exchanges, virtual museum tours, and social media campaigns now complement traditional programs.
Virtual reality lets people experience cultural sites from anywhere. Museums offer immersive online tours while festivals stream performances globally.
Social media influencers share authentic cultural experiences with millions of followers. Digital arts projects connect creators worldwide, and online language platforms make cultural education accessible to everyone.
Streaming services have become cultural export tools, with countries creating content that showcases their lifestyles to an international audience.
These digital tools make cultural diplomacy more affordable and accessible, enabling smaller nations to compete with major powers.
Final Thoughts
Cultural diplomacy demonstrates that nations can foster stronger relationships through shared human experiences, rather than relying solely on formal agreements.
From student exchanges to art exhibitions, these programs create lasting bonds between people and countries. While traditional diplomacy handles immediate crises, cultural diplomacy plants seeds for long-term understanding and cooperation.
The most successful countries combine both approaches, using cultural connections to support their broader diplomatic goals. As our world becomes increasingly connected, cultural diplomacy will continue to grow in importance.
What cultural exchange experience has most influenced your view of another country? Share your thoughts in the comments below.