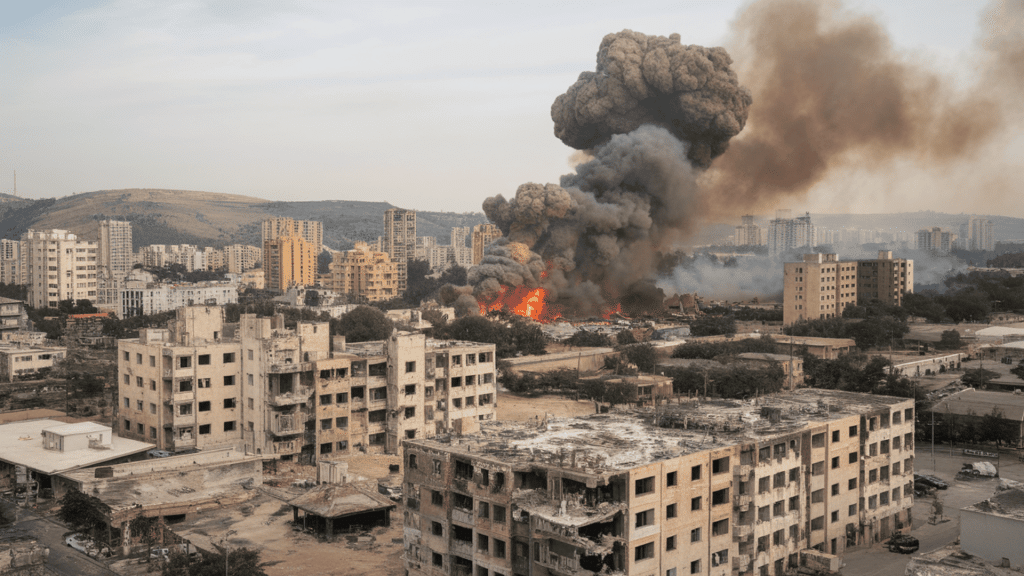
Why do wars keep erupting across the world, despite our progress in communication and diplomacy? From border disputes to civil wars, global conflicts continue to shape our headlines.
Knowing the causes of global conflicts helps us make sense of why nations clash and communities divide.
Wars don’t start overnight. They grow from deep-rooted issues that build tension over time. In this blog, I’ll show you the main factors that spark wars around the world.
You’ll learn about political, economic, social, and environmental causes that drive nations into conflict.
What Is a Global Conflict?
A global conflict is a large-scale dispute that affects multiple countries or regions. These conflicts often involve wars, political tensions, or economic disputes that cross international borders.
Global conflicts have shaped human history for centuries. From ancient empires fighting for territory to modern nations competing for resources, these disputes continue to impact millions of lives.
Some conflicts last for years, while others end quickly through diplomacy or military action.
These conflicts can range from world wars involving many nations to regional disputes that impact neighboring countries.
The reasons behind these conflicts help us learn why some areas face repeated problems while others remain peaceful.
Major Causes of Global Conflicts
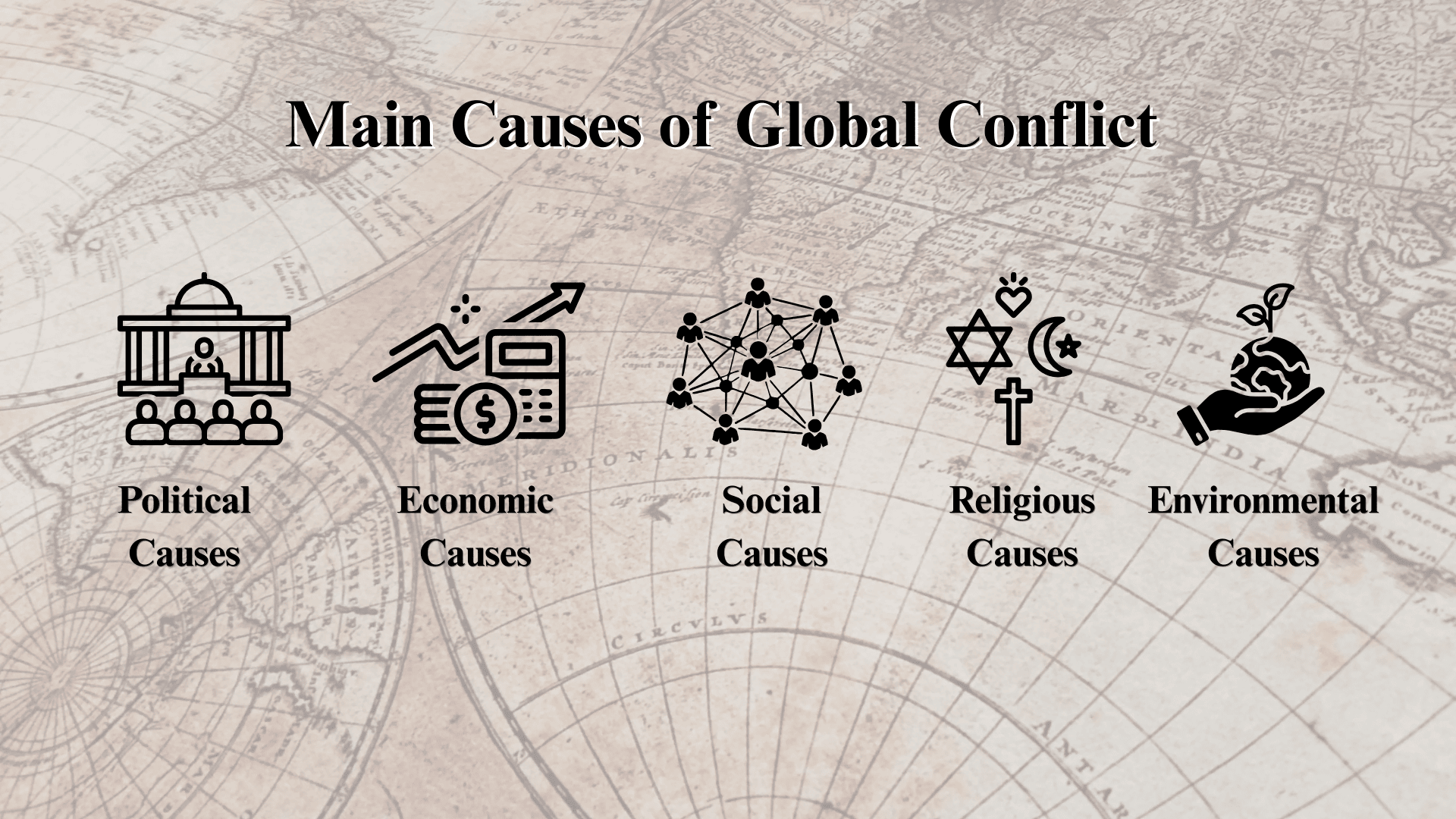
Global conflicts don’t happen by chance. They begin when various factors accumulate over time and create tensions between nations or groups.
These main causes of global conflicts can work alone or combine with other issues to spark violence.
Let’s examine the key factors that drive countries and communities into conflict worldwide.
1. Political Causes
Political factors are among the most common triggers for international wars. Governments clash when their interests don’t align or when they compete for influence.
Key political causes include:
- Territorial disputes: Nations fight over land, borders, and strategic locations.
- Power struggles: Leaders seek to expand their control or influence over other countries.
- Failed diplomacy: When peaceful talks break down, military action often follows.
- Weak governments: Unstable states create power vacuums that others try to fill.
- Alliance conflicts: When allied nations get pulled into each other’s disputes.
- Succession issues: Fights over who controls a country after leadership changes.
Political tensions often start small but can grow into major international crises. Border disagreements between neighboring countries frequently escalate into armed conflicts.
2. Economic Causes
Money and resources drive many global conflicts. When nations compete for economic advantages, tensions can quickly turn violent.
Major economic causes include:
- Resource competition: Fighting over oil, minerals, water, and fertile land
- Trade disputes: Disagreements over markets, tariffs, and economic policies
- Economic inequality: Large gaps between rich and poor nations create resentment
- Debt and financial pressure: Economic stress can push countries toward aggressive actions
- Control of trade routes: Nations fight for strategic shipping lanes and commercial pathways
- Industrial competition: Countries clash when trying to dominate specific industries
Economic factors often combine with political issues. When a nation’s economy struggles, leaders may blame other countries and seek military solutions.
3. Social and Cultural Causes
Differences between groups of people can spark serious conflicts. When communities don’t understand or accept each other, violence may follow.
Social and cultural factors include:
- Ethnic tensions: Conflicts between different racial or cultural groups
- Language barriers: Communication problems that create misunderstanding
- Historical grudges: Old conflicts that create lasting hatred between groups
- Migration issues: Tensions when large groups of people move to new areas
- Social inequality: Unfair treatment based on race, class, or background
- Cultural preservation: Fighting to protect traditional ways of life
These social issues often simmer for years before exploding into open conflict. Different groups may live peacefully together until economic or political stress makes tensions worse.
4. Religious and Ideological Causes
Beliefs about religion, politics, and how society should work can divide nations. When groups hold completely different worldviews, compromise becomes difficult.
Religious and ideological causes include:
- Religious differences: Conflicts between different faith communities
- Political ideologies: Fights between competing systems of government
- Extremist movements: Radical groups that use violence to spread their beliefs
- Sacred sites: Disputes over religious locations important to multiple groups
- Missionary activities: Tensions when one group tries to convert others
- Secular vs. religious: Conflicts between religious and non-religious worldviews
These belief-based conflicts are often the hardest to resolve. When people feel their core values are under attack, they may fight fiercely to defend them.
5. Environmental and Resource-Driven Causes
Environmental problems create new sources of conflict around the world. As resources become scarce, competition increases between nations and communities.
Environmental causes include:
- Water scarcity: Fighting over rivers, lakes, and underground water sources
- Climate change effects: Conflicts caused by droughts, floods, and changing weather
- Food security: Competition for farmland and fishing areas
- Natural disasters: Conflicts that arise when disasters destroy resources
- Pollution disputes: Disagreements over environmental damage across borders
- Resource depletion: Fighting over the last supplies of valuable materials
Environmental conflicts often affect the poorest countries the most. When basic needs like water and food become scarce, desperate communities may turn to violence.
Conflict Resolution & Prevention Strategies
Once conflicts begin, ending them requires different strategies than those used for prevention. Below are the successful resolutions that focus on addressing root causes while building lasting peace.
| Resolution Method | Description | How It Works |
|---|---|---|
| Ceasefire agreements | Stopping the fighting to create space for peace talks | Both sides must agree to halt military actions while negotiations begin |
| Peace negotiations | Formal talks where parties discuss concerns and find solutions | Skilled mediators help guide these conversations toward fair agreements |
| Truth and reconciliation | Addressing past wrongs to help communities heal together | Victims tell their stories while perpetrators take responsibility for their actions |
| Post-conflict reconstruction | Rebuilding infrastructure and creating stable institutions | International aid helps restore schools, hospitals, and government systems |
| Disarmament programs | Removing weapons and helping former fighters build new lives | Ex-combatants receive job training and education to start fresh |
The most successful peace processes address both immediate violence and long-term causes. Countries that invest in education and fair governance create lasting stability.
Conclusion
The causes of global conflicts are complex and interconnected. Political disputes, economic competition, social tensions, religious differences, and environmental pressures all play important roles.
Understanding these main reasons for global conflicts helps us recognize warning signs and work toward peaceful solutions.
No single factor creates war on its own. Instead, multiple causes build up over time until tensions explode. By addressing root problems early, countries can prevent small disagreements from becoming major conflicts.
Which cause do you think has the biggest impact on today’s world? Share your thoughts in the comments.