Ever wondered why gas prices shoot up during summer road trip season, or why your favorite concert tickets cost a fortune?
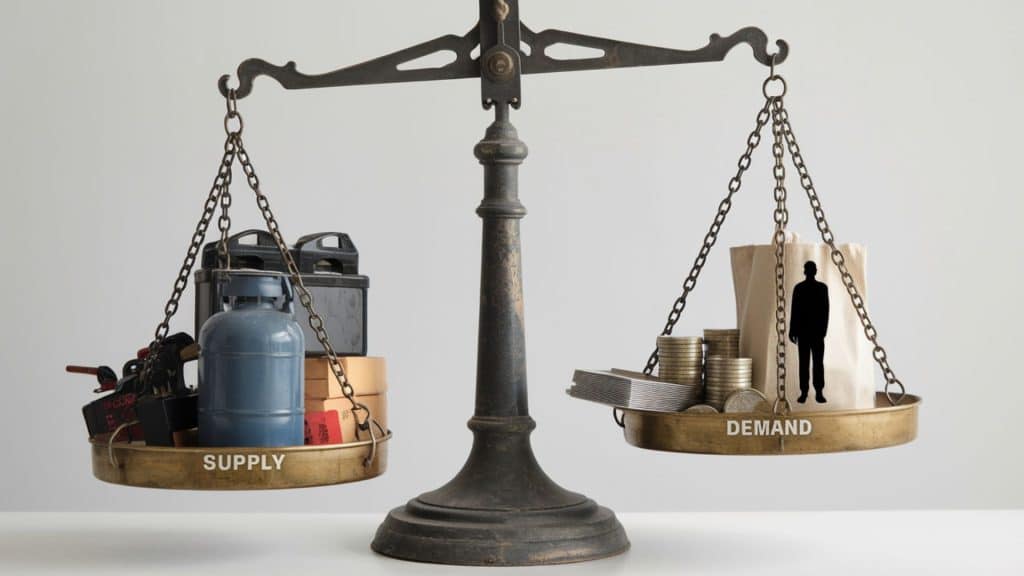
The answer lies in the fascinating interplay between supply and demand, two of the most powerful forces shaping our economy.
These invisible hands determine everything from the price of your morning coffee to the cost of buying a home. But what exactly makes supply go up or down? What pushes demand in different directions?
Understanding Supply and Demand Basics
Before diving into the factors, let’s briefly clarify what we’re discussing.
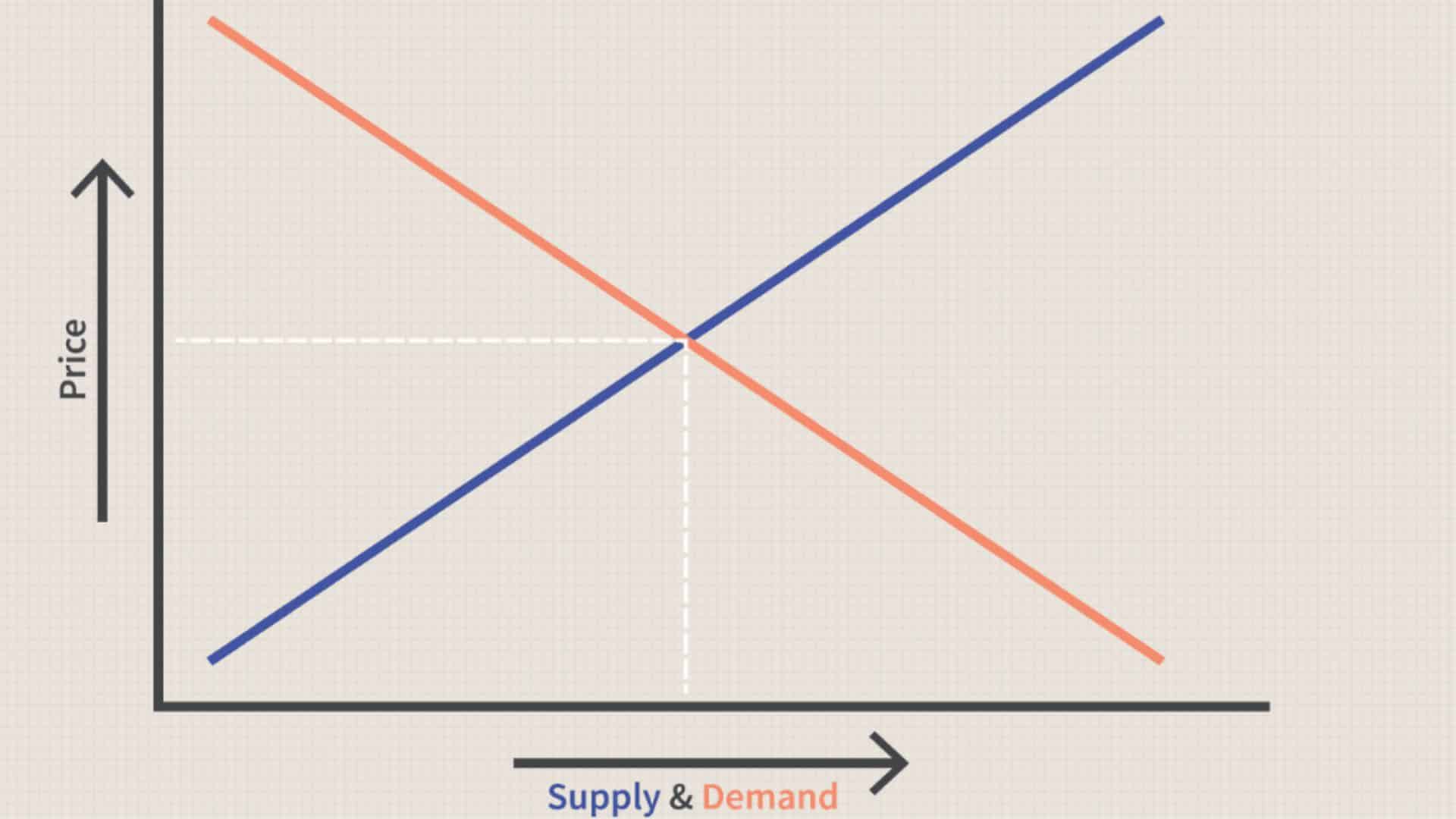
Supply refers to the quantity of a product or service available in the market.
Demand represents the amount that consumers want and can afford to purchase.
When supply is high and demand is low, prices drop. When demand is high and supply is low, prices rise. It’s that simple – yet the factors behind these shifts are surprisingly complex.
Key Factors Affecting Supply

1. Production Costs
One of the biggest drivers of supply is the cost of production. When production costs rise, companies often reduce supply to maintain profits.
Main cost factors include raw material prices, labor wages, energy costs, equipment, and machinery expenses.
For example, if steel prices increase, car manufacturers may reduce production, thereby lowering the supply of vehicles on the market.
2. Government Regulations
Rules and regulations impact supply in different ways. Safety standards can raise costs and lower supply, while tax incentives may boost production.
Key regulatory factors include environmental rules, safety requirements, trade restrictions, and tax policies.
3. Technology Advances
Technology can dramatically boost supply by making production faster, cheaper, or more efficient. Think about how automation has increased manufacturing capacity across industries.
Technology impacts supply through:
- Improved manufacturing processes
- Better resource utilization
- Reduced waste and errors
- Faster production speeds
4. Weather and Natural Conditions
Weather plays a huge role, especially in agriculture and energy. A drought can devastate crop supply, while perfect growing conditions can create abundance.
Extreme weather events, such as storms or floods, can also disrupt production and supply chains, leading to price fluctuations and shortages.
Climate patterns and seasonal changes further add to the unpredictability affecting supply levels.
5. Number of Suppliers
More competitors in a market typically mean a higher overall supply of goods and services. When new companies enter an industry, total market supply usually increases.
This often leads to a greater variety of products and competitive pricing, benefiting consumers. However, intense competition can also pressure profit margins and drive innovation among existing players.
Major Factors Affecting Demand
Demand is influenced by a variety of key factors that determine how much consumers are willing and able to buy. Understanding these drivers helps explain changes in market behavior and price fluctuations.
1. Consumer Income Levels
When people have more money, they tend to buy more things. It’s straightforward – higher income generally leads to higher demand for goods and services.
Income affects demand in two ways:
- Normal goods: Demand increases as income rises (like dining out)
- Inferior goods: Demand decreases as income rises (like generic brands)
2. Population Changes
A growing population naturally increases demand, as more people need goods and services.
Changes in age groups, where people live, and cultural tastes also shape what products and services are in demand, influencing market trends and business strategies.
3. Consumer Preferences and Trends
What people want changes over time. Social media, celebrity endorsements, and cultural shifts can dramatically alter demand patterns.
Preference drivers include:
- Fashion and style trends
- Health and wellness awareness
- Environmental consciousness
- Social media influence
4. Prices of Related Products
The demand for a product is often influenced by the prices of related goods.
Substitute goods, such as coffee and tea, can experience a shift in demand when one becomes more expensive. Similarly, complementary goods, such as gasoline and cars, are connected; if gas prices rise, people may buy fewer cars.
5. Future Expectations
What consumers expect to happen tomorrow affects what they buy today. If people anticipate that prices will rise, they may buy more now.
Expectation factors: Anticipated price changes, economic outlook, job security concerns, and seasonal expectations
External Forces That Impact Both Supply and Demand
External forces can significantly influence both supply and demand, often causing shifts in market balance.
| Factor | Impact on Demand | Impact on Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Conditions | Demand usually drops during recessions due to lower consumer spending | Supply can decline as businesses close or cut production |
| Government Policies | Tax changes and subsidies can increase or decrease consumer demand | Policies influence production costs and supply availability |
| Global Events | Events like pandemics and trade wars disrupt consumer buying habits | Supply chains can be delayed or disrupted globally |
| Seasonal Patterns | Demand rises and falls predictably (e.g., ice cream in summer) | Supply adjusts to seasonal demand changes (e.g., winter coats) |
These external factors often work together, creating complex shifts in both supply and demand. Understanding them helps businesses and consumers make better economic decisions.
Real-World Examples
Let’s look at how these factors play out in real markets:
Housing Market:
- Supply factors: Construction costs, available land, building regulations
- Demand factors: Interest rates, population growth, income levels
Gasoline Market:
- Supply factors: Oil prices, refinery capacity, seasonal blends
- Demand factors: Driving patterns, vehicle efficiency, economic activity
Smartphone Market:
- Supply factors: Technology advancement, component costs, manufacturing capacity
- Demand factors: Upgrade cycles, new features, competitor pricing
The Bottom Line
The factors affecting supply and demand are everywhere around us, constantly shaping the prices we pay and the choices we make.
From production costs and technological advances to consumer income and global events, these forces interact in complex ways that determine market outcomes.
By understanding these factors, you can better anticipate price changes, make more informed purchasing decisions, and gain valuable insight into how the economy really works.
The next time you see a price increase or shortage, you’ll know exactly what forces might be at play behind the scenes.
For more information on the economy, please visit our website.