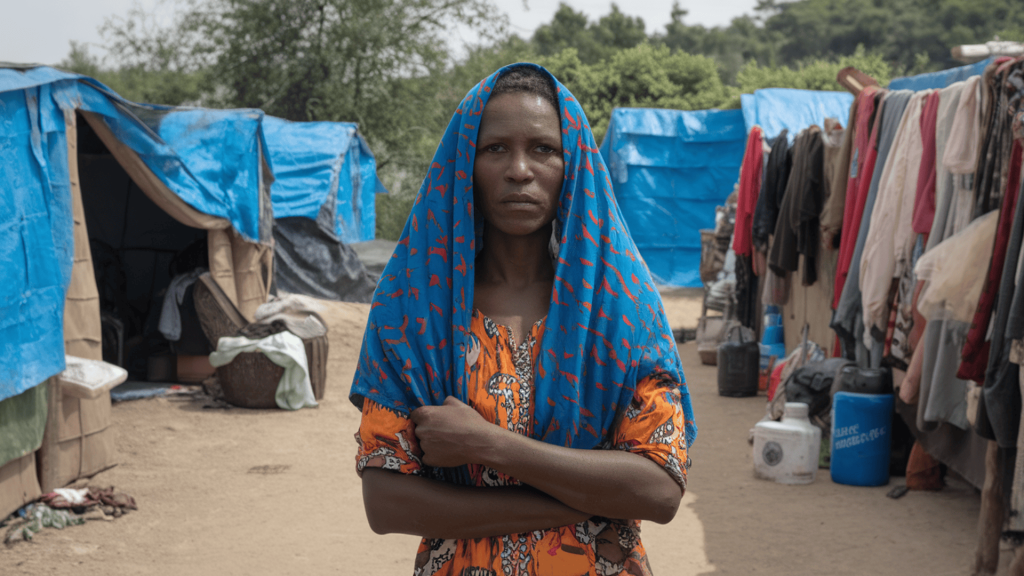
Have you ever wondered why millions of people leave everything behind to seek safety in foreign lands?
The global refugee crisis affects over 100 million displaced people worldwide.
These numbers represent real families torn from their homes by war, persecution, and disasters.
In this blog, I’ll outline the primary causes of refugee crises, the challenges faced by displaced people, and practical solutions that can make a tangible difference.
Let’s explore this global humanitarian challenge.
What Is a Refugee Crisis?
A refugee crisis occurs when large numbers of people are forced to leave their home countries due to persecution, war, violence, or human rights violations.
Unlike migrants who choose to move, refugees have no safe option but to flee for their survival.
The 1951 Refugee Convention defines a refugee as someone who cannot return to their home country due to a well-founded fear of persecution based on race, religion, nationality, political opinion, or membership in a social group.
When these situations affect thousands or millions simultaneously, it becomes a crisis requiring an international response.
Today’s refugee situations are more complex than ever.
Climate change, economic collapse, and prolonged conflicts create new patterns of displacement that traditional definitions struggle to address.
Main Causes of Refugee Crises
Understanding what causes the refugee crisis helps us address the root problems. People flee their homes for different reasons, but four main factors drive most displacement worldwide.
Each cause creates unique challenges that require specific responses.
1. War and Armed Conflict

Armed conflicts remain the primary driver of forced displacement worldwide. When wars break out, civilians face immediate threats to their lives and safety.
Key points:
- Syria, Afghanistan, and Ukraine have seen millions flee due to ongoing violence
- Families abandon homes, schools, and jobs to escape bombing and crossfire
- Civil wars create complex situations with no safe zones within countries
2. Persecution and Human Rights Violations

Systematic persecution forces people to flee when governments or societies target them. This includes religious minorities, ethnic groups, political opponents, and LGBTI+ individuals.
Examples include:
- Government crackdowns are pushing activists and journalists to seek safety
- Historical cases like the Holocaust and the Rwandan genocide
- Ongoing persecution of Rohingya Muslims in Myanmar
3. Climate Change

Environmental factors increasingly drive people from their homes. Rising sea levels, droughts, floods, and extreme weather destroy livelihoods and make areas uninhabitable.
Impact areas:
- Small island nations are facing complete submersion
- Sub-Saharan farmers abandoning drought-destroyed farmland
- Both sudden displacement from disasters and gradual environmental migration
4. Economic Collapse and Poverty

Severe economic crises force people to leave when basic needs become impossible to meet. While not traditional refugees, extreme poverty often creates conditions similar to those of refugees.
Venezuela example:
Economic collapse has driven over 7 million people from their country due to hyperinflation, food shortages, and the collapse of public services.
Key Challenges That Refugees Face
Displaced people encounter numerous obstacles that affect every aspect of their lives:
- Safety concerns: Dangerous border crossings, exploitation by smugglers, and ongoing threats in host countries
- Lack of shelter: Overcrowded camps, inadequate housing, and homelessness in urban areas
- Limited healthcare access: No insurance, language barriers, and overwhelmed medical systems
- Education disruption: Children missing school, language barriers, and lack of recognized credentials
- Employment restrictions: Legal barriers to working, exploitation, and skills not matching job markets
- Social discrimination: Racism, xenophobia, and cultural misunderstandings in host communities
These challenges create cycles of vulnerability that can last for generations. Without proper support, refugees struggle to rebuild their lives and make meaningful contributions to their new communities.
Global Responses and Solutions
Addressing refugee crises requires coordinated efforts from governments, organizations, and communities. Multiple approaches work together to provide immediate relief and long-term solutions for displaced people.
| Response Type | Examples | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Policy Solutions | Refugee conventions, asylum laws, integration programs | Legal protection, clear processes |
| Humanitarian Aid | UN agencies, NGOs, and emergency assistance | Immediate relief, basic needs |
| Resettlement Programs | Third-country resettlement, sponsorship | Permanent solutions, family reunification |
| Community Integration | Language classes, job training, cultural programs | Long-term stability, social cohesion |
International cooperation remains essential for effective responses. No single country can address refugee situations alone.
Burden-sharing agreements, financial support, and coordinated policies help distribute responsibility fairly.
How Can Individuals Help in a Crisis?
Everyone can contribute to supporting refugees through various meaningful actions:
- Financial support: Consider donating to established organizations such as UNHCR, local refugee resettlement agencies, or community support groups.
- Volunteer time: Help with English tutoring, job interview preparation, or cultural orientation programs in your area.
- Advocacy efforts: Contact elected representatives, participate in awareness campaigns, and support policies that protect the rights of refugees.
- Community building: Welcome refugee families, participate in cultural exchange programs, and combat discrimination through education.
Small actions add up to significant impact. Sharing accurate information about refugees helps counter misinformation and fosters more welcoming communities.
Conclusion
Global refugee crises stem from complex causes, including conflict, persecution, climate change, and economic collapse.
Effective solutions require both immediate humanitarian responses and long-term approaches that address the root causes.
While governments lead large-scale responses, individuals can make meaningful contributions through donations, volunteering, and advocacy.
Understanding refugee experiences helps build more compassionate responses.
What steps will you take to support refugees in your community? Share your thoughts about addressing this global humanitarian challenge.